Orthopedic
Treating Musculoskeletal Disorders
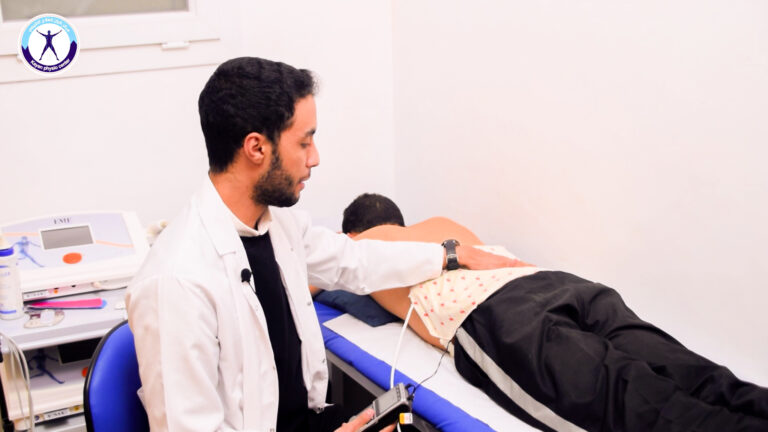
Orthopedic medicine focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of musculoskeletal disorders, including conditions affecting bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Orthopedic treatments range from non-invasive methods, such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications, to surgical interventions like joint replacement, fracture repair, and ligament reconstruction. Patients may seek orthopedic care for a variety of reasons, including sports injuries, age-related degenerative conditions like arthritis, or congenital musculoskeletal deformities. The goal of orthopedic care is not only to relieve pain but also to restore function, improve mobility, and enhance quality of life. Post-operative rehabilitation plays a key role in the recovery process, with tailored programs designed to restore strength, flexibility, and coordination to support long-term joint and bone health. Through a combination of preventive measures, conservative treatments, and advanced surgical techniques, orthopedics aims to help individuals regain independence and return to their daily activities.